Bronchitis – Symptoms and Treatment
What is Bronchitis?
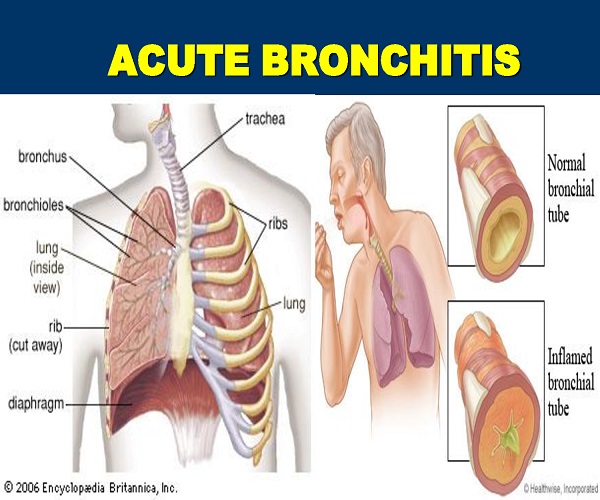
Image : Source
Our bronchial tubes perform the important function of carrying the air that we breathe in from the trachea to the lungs. Bronchitis is a disease of the respiratory tract where the mucus membrane in the bronchial tubes gets inflamed due to a viral or bacterial infection. As a result of the swelling the passageway narrows leading to bouts of coughing. If it is a mild case of bronchitis then one recovers quickly. But if the bronchitis develops into a chronic one then it can be a long drawn process requiring medical intervention.
Types of Bronchitis
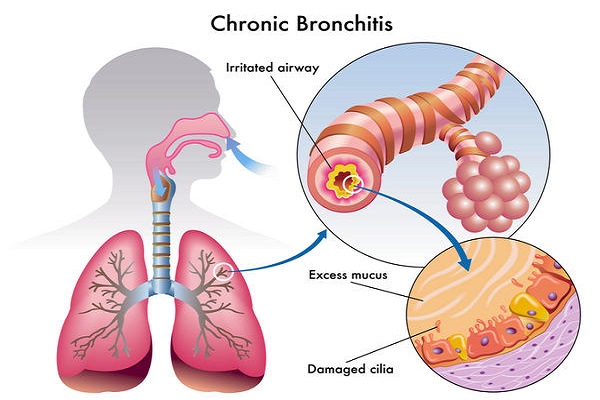
Image : Source
Bronchitis is of two types – acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is a lung infection where the large bronchi in the lungs get inflamed due to a viral or a bacterial infection. This condition can last for a few days to about less than three weeks. Here the main symptom is coughing which could be accompanied by other symptoms such as wheezing or chest pain.
In chronic bronchitis the symptoms are the same but here the coughing lasts for more than three months and can continue for years on end. Chronic bronchitis is more common in people who smoke. Millions of cilia within the bronchi perform the important function of sweeping out the harmful stuff. Cigarette smoke damages these cilia and prolonged smoking damages these cilia such that they stop functioning altogether. The airways remain permanently clogged with mucus which leads on to further respiratory illnesses such as lung infections and COPD.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis is more commonly caused by viruses; however bacteria might sometimes cause bronchitis too. Irritants like tobacco smoke, noxious fumes, gases, air pollutants might aggravate your condition. The symptoms of bronchitis in some way resembles that of common cold thus there might be a confusion in diagnosis but doctors have the expertise to make an accurate judgment based on the symptoms.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
1. Coughing
Coughing is by far the most common symptom for bronchitis. If your cough continues for more than 5 days in a row then you have acute bronchitis. If the cough persists for more than 3 months and continues for at least 2 years then it is a case of chronic bronchitis. The cough is often accompanied by sputum. The color of the sputum may vary from being a light color to sometimes being yellow or green. This persistent cough continues throughout the night whereby a patient has difficulty sleeping through the night. In winter this condition worsens further.
2. Sore Throat
Sore throat is another symptom of bronchitis. An individual might have pain swallowing or talking which is sometimes accompanied by a dry scratchy sensation in the throat.
3. Fever
In acute bronchitis you might sometimes have a low grade fever. But if you get a high fever and see your condition worsening then it is safe to consult a doctor.
In addition to the above symptoms, patients might also experience headaches, body pain and a general feeling of ill-being.
Preventive Measures
By following certain preventive measures you can stop aggravation of the symptoms.
• Wear masks when you are going out to protect yourself from pollutants that cause bronchitis.
• Smoking is a major cause of chronic bronchitis, so quit smoking now.
• Go easy on that cough syrup. A productive cough where you cough up mucus is actually good as it is the body’s way of getting rid of the excessive mucus. In case your cough is disrupting your normal life, then take a cough expectorant.
• Stay hydrated by drinking adequate fluid.
• Take adequate rest.
• Stay away from foods that increase cough like fatty foods and sugar-laden foods.
• Use a humidifier to loosen up the mucus. You could also go for a home remedy of steam inhalation. This provides considerable relief.
• Be sure to take your yearly flu vaccinations. They can prevent bronchitis. Additionally take a pneumonia vaccine too.
• Maintaining personal hygiene goes a long way in protecting oneself against viral and bacterial infections.
• Stay away from noxious fumes and smoke as they might aggravate your condition.
Treatment Options
One look at your symptoms and your doctor can easily determine whether you have bronchitis or not. Routine treatment for acute bronchitis is almost the same as that for normal flu. Taking adequate rest and increasing the amount of fluid intake is recommended. If your cough is bothering you then you take a cough expectorant but only on the recommendations of your doctor. For fevers and body aches you can take acetaminophen. If by chance your bronchitis is due to a bacterial infection or the doctor suspects a lung infection then you will have to take antibiotics.
If the doctor suspects you of having chronic bronchitis then you would have to get an X-ray of the chest done to determine the extent of lung damage. In cases of COPD along with chronic bronchitis the lungs ability to deliver oxygen to the body gets restricted. Here the patient has difficulty in breathing as the airways are clogged. In such cases, you would have to take bronchodilator medicines which opens up the airways and enables free breathing. Sometimes steroids are also given to patients to facilitate breathing. In certain cases, your doctor might even recommend an oxygen therapy for you. Depending on the severity of the condition, this could be either on a continuous basis or as and when required.