Diabetes 1 – Symptoms and Prevention
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Diabetes 1 or Diabetes Mellitus is a form of diabetes where the insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas is destroyed resulting in the body producing insufficient insulin. Insulin is a hormone which is required to convert sugar and starch into energy since our body cannot directly utilize the sugar/glucose per se. The lack of insulin in the body leads to increased presence of glucose in the blood and urine leading to diabetes. The most common symptoms are frequent urination, increased hunger and weight loss. Since diabetes 1 is usually prevalent in children and young adults it is also known by the name of juvenile diabetes. Controlling diabetes is a must as unchecked blood glucose levels in the blood might lead to severe health complications.
Causes
What causes diabetes 1 is still unknown till today but certain theories abound regarding the onset of diabetes 1. Genetics might play a role in diabetes. If a close family member of yours has diabetes, chances are you might develop this disease. Race could also be a determining factor.
One theory suggests that a certain toxin triggers our body’s defense system. In the process of destroying the toxin, our body inadvertently begins destroying the beta cells. Destruction of beta cells means lessened insulin production. As a result of this glucose is not absorbed by the body leading to sugar accumulation in the blood. The body deprived of lack of energy will then begin to break down proteins and fats to provide energy to the food-starved cells. In the meantime, sugar levels increase in the blood leading to diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes-1
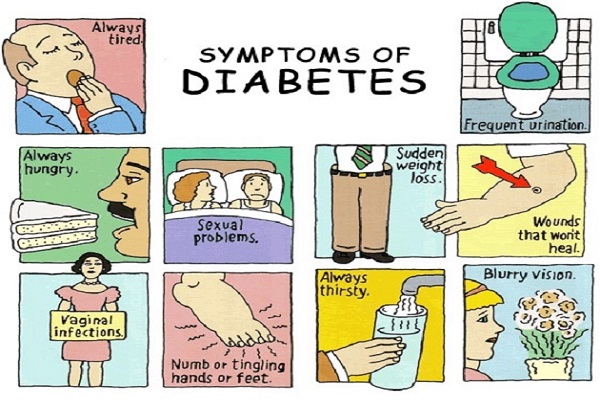
Image : Source
1. Frequent Urination
This is one of the most common symptoms of diabetes with frequent urination being a big issue with diabetic patients. Since the body has no use of the excess glucose moving about in our blood, our kidneys take on the responsibility of removing them. In order to remove the excess sugar the kidneys utilize more water which essentially means frequent urination.
2. Always feeling Thirsty
Diabetes can also result in a feeling of thirst and a sensation of being dehydrated. Frequent urination means excess loss of water from the body with there being a possibility of dehydration. In order to make up for the water loss our body feels the urge to replenish it and thus we feel thirstier. Thus one feels the need to drink water every now and then.
3. Tired Feeling
Glucose is the main energy source for our body. But if you suffer from diabetes, your body is unable to utilize the glucose leading to a feeling of being tired and exhausted often.
4. Weight Loss
In diabetes, our body is unable to fully process the glucose as most of it is excreted out in the form of urine. To meet our requirement the body breaks down other energy sources such as fats leading to weight loss. Also the food that was meant to reach our cells never reaches them, so a diabetic patient also feels hungry often.
5. Frequent Infections
It is seen that people with diabetes develop infections more often. Though there is no conclusive research proving this fact, it is hinted that the high glucose levels in the blood might interfere with the body’s natural healing mechanism and its ability to stave off infections. This essentially means that not only your sores heal slowly but you also get infected quickly.
6. Tingling hands and feet
Large amounts of sugar in the blood leads to a condition called neuropathy where there is a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. This sensation generally starts at the toe and gradually progresses towards the arms.
7. Blurred Vision
Excess sugar in the blood sometimes leads to eye problems such as the build-up of excess fluid in the lens of the eye. This change in shape of the lens leads to blurred vision. This can be corrected by stabilizing one’s blood sugar levels. Neglecting it might however result in serious complications such as glaucoma, cataract and even blindness.
How to diagnose Type -1 Diabetes?
Diabetes 1 can be diagnosed by taking a fasting blood glucose test. If the fasting blood glucose is above 126 mg/dL then it is a confirmed case of diabetes. Anything in between 100-125 mg/dL is regarded as a pre-diabetic stage.
Complications
Ignoring the symptoms of diabetes 1 can lead to several complications such as:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a condition which can occur in people suffering from diabetes 1. In diabetes 1 the body produces less insulin, thus the body resorts to utilizing fatty acids to produce energy. Breakdown of fatty acids leads to the production of ketone bodies which in excess levels can be toxic leading to nausea, severe dehydration or cerebral edema. If the condition continues a person might land in coma and even die.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood sugar levels falls below 70 mg/dL. Younger children are more at risk of developing hypoglycemia as they are unable to understand the symptoms. Symptoms generally include trembling, hunger pangs, rapid heartbeat and sweating.
Heart Disease
Patents suffering from diabetes are more prone to heart diseases and strokes than healthy patients. In diabetes, if perchance the kidneys are damaged then the person can also suffer from high blood pressure. High blood pressure or hypertension can contribute to heart attacks or strokes. Atherosclerosis progresses in a person suffering from diabetes leading to an increased incidence of heart diseases.
Neuropathy
Diabetes disturbs the normal functioning of the nerves leading to a condition called neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy – a condition where the nerves in the toes, arms, and feet are affected is generally more prevalent among diabetics. The most common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are a tingling sensation, burning sensation and a feeling of numbness in the affected body parts.
Treatment Options

Image : Source
Insulin Doses
Since the body has stopped producing insulin the patient has to take insulin doses to keep their blood sugar levels in a manageable range. One could take insulin injections but if you do not like the idea of a needle sticking into your body every now and then you can opt for a painless method in the form of insulin pumps. This is not only a painless method but is also a very accurate way of delivering insulin doses.
Maintain a Proper Diet
Persons with type 1diabetes have to eat food regularly to prevent undue fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Drawing up a chart of healthy foods conducive to a diabetic condition would be a big help.
Foot Care
In type 1 diabetes, the nerves of the feet can be damaged. Even a minor cut on the feet can turn infectious and develop into a serious problem. Peripheral damage to the nerves of the feet results in numbness which might further compound the problem as the patient might not even be aware of the wound in his feet. Neglect of the wound might result in an infection which might further develop into an ulcer. In extreme cases, it might also result in the affected foot being amputated. It is therefore necessary that a patient not only take proper care of his feet but also bring to the attention of his doctor any wound or injury to their feet.


